What Is A Lithium Battery Separator?
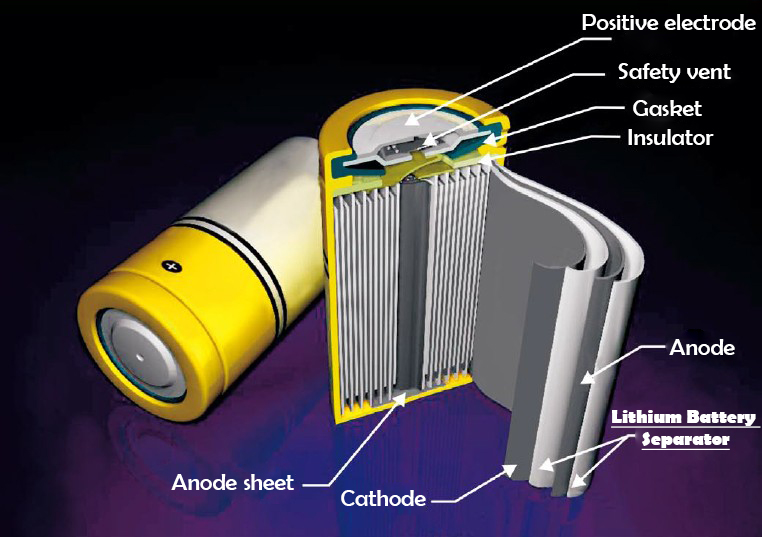
The lithium battery separator is one of the key inner layer components in the structure of the lithium battery, and a high-strength thin-film polyolefin porous membrane is generally used. The performance of the separator determines the interface structure and internal resistance of the battery, which directly affects the capacity, cycle, and safety performance of the battery. The separator with excellent performance plays an important role in improving the overall performance of the battery.
Performance of Lithium Battery Separator
The separator is located between the positive electrode and the negative electrode, and its main function is to separate the positive and negative active materials to prevent the two electrodes from being short-circuited due to contact; in addition, during the electrochemical reaction, it can maintain the necessary electrolyte and form a channel for ion movement. The diaphragm material is non-conductive, the type of battery is different, and the diaphragm used is also different. For lithium-ion batteries, since the electrolyte is an organic solvent system, the separator is required to have the following properties:
①In the battery system, its chemical stability needs to be good, and the materials used are resistant to organic solvents.
②High mechanical strength and long service life.
③ The ionic conductivity of the organic electrolyte is lower than that of the aqueous system. In order to reduce the resistance, the electrode area must be as large as possible, so the diaphragm must be very thin.
④When the battery system is abnormal, the temperature rises. In order to prevent danger, when the rapid heat generation temperature (120~140℃) begins, the thermoplastic diaphragm melts, the micropores close, and it becomes an insulator, preventing the electrolyte from passing through, so as to achieve The purpose of interrupting the current.
⑤ From the perspective of lithium batteries, they must be fully impregnated with organic electrolytes and can maintain a high degree of impregnation during repeated charge and discharge processes.
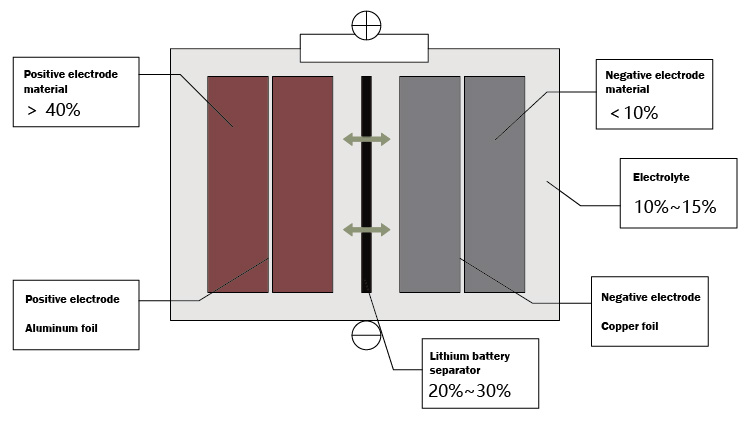
Commonly used separator materials in batteries are microporous membranes made of cellulose or braided fabrics and synthetic resins. Lithium-ion batteries generally use high-strength, thin-film polyolefin-based porous membranes. Commonly used separators include polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE) microporous separators, as well as copolymers of propylene and ethylene, polyethylene homopolymers, etc.
Requirements for Lithium Battery Separator
①It has electronic insulation to ensure the mechanical isolation of positive and negative electrodes.
②It has a certain pore size and porosity to ensure low resistance and high ionic conductivity and has good permeability to lithium ions.
③ Since the solvent of the electrolyte is an organic compound with strong polarity, the diaphragm must be resistant to corrosion by the electrolyte and have sufficient chemical and electrochemical stability.
④ It has good wettability to electrolyte and has sufficient liquid absorption and moisturizing ability.
⑤ Have sufficient mechanical properties, including puncture strength, tensile strength, etc., but the thickness is as small as possible.
⑥ Good spatial stability and flatness.
⑦Good thermal stability and automatic shutdown protection performance. Power batteries have higher requirements for separators, and composite membranes are usually used.
The Material of Lithium Battery Separator
The market-oriented diaphragm materials are mainly polyolefin diaphragms based on polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP). Among them, PE products are mainly made by wet process, and PP products are mainly made by dry process.
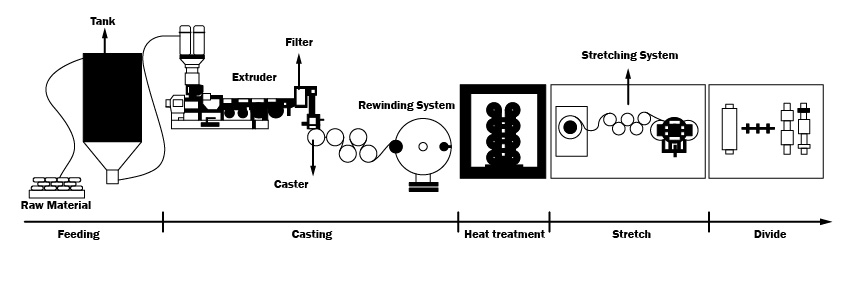
The preparation process of the diaphragm – Dry Method – Uniaxial Stretching
①Feeding→②Casting→③Stretching→④Shaping and Winding
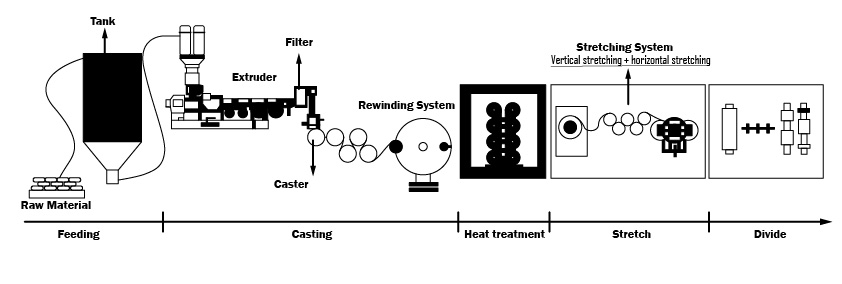
The preparation process of the diaphragm – Dry Method – Two-way Stretch
China’s unique diaphragm manufacturing process.
①Feeding→②Casting→③Vertical stretching→④Horizontal stretching→⑤Shaping and Winding
Comparision of the characteristics of the two processes:
| Process method | Unidirectional stretch | Two-way stretch |
| Process principle | Chip stretching | Chip Transformation |
| Method features | 1)The equipment is complex2)The precision is high3)The investment is large4)The control is difficult5)The environment is friendly | 1)The equipment is complex 2)The investment is large 3)Auxiliary additions such as pore-forming agents are generally required |
| Features | 1)Micropore size2)Uniform distribution3)Good micropore permeability4)Poor lateral thermal shrinkage of the product5)Can produce products of different thicknesses | 1)Pore size2)Uniform distribution3)Better air permeability 4)Poor stability |
The preparation process of the diaphragm – Wet Method
The wet method, also known as the phase separation method or the thermally induced phase separation method, adopts biaxial stretching. At present, the global manufacturers of diaphragms mainly use the wet method.
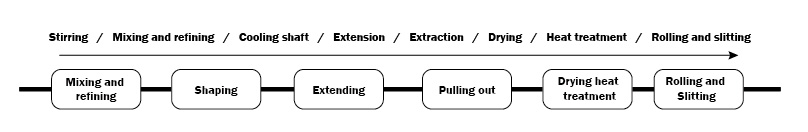
Wet process product features
The micropores are small in size and evenly distributed, suitable for the production of thinner products, only PE products can be produced.
As for the characteristics of the two materials, PE and PP, they have their own advantages and disadvantages. In general:
①PP is relatively more resistant to high temperature, and PE is relatively resistant to low temperature;
②PP density is smaller than PE;
③PP melting point and closed-cell temperature are higher than PE;
④PP products are more brittle than PE;
⑤PE is more sensitive to environmental stress.
The main diaphragm material products are single-layer PP, single-layer PE, PP+ceramic coating, PE+ceramic coating, PP+PP/PE, PP+PP/PP, and PP+PP+PP/PE/PP, among which the first two types of products are (Single-layer PP, single-layer PE) are mainly used in the field of 3C small batteries, and the latter types of products are mainly used in the field of power lithium batteries.
Lithium battery separator material products show a clear trend of diversification.
